Important Guidelines for Copy Editing
Your book is your baby. You want it to look the best it can and convey your message in the most understandable and clear way. The best way to ensure this is to contract a professional editor to look over your manuscript. When interviewing editors, be sure and choose one who uses the standards outlined in a recommended style guide. The Chicago Manual of Style is the most widely accepted in the publishing industry.
There are two different types of editing:
- Developmental editing is where an editor takes your work, and then completely reworks it to be what they think is best. They may also work hand-in-hand with you to write the book. There are times you may want this type of service, but it can be costly when self-publishing. This is the type of editing most common with traditional publishers.
- Copy editors take your work and go over it with a fine-toothed comb searching for spelling and grammar errors, correct use of punctuation, etc. They know what to look for to make your manuscript look consistent and professional.
You can save money on copy editing if you follow these self-editing techniques before handing your manuscript over to an editor.
- Double-spacing after sentences—Correct computer spacing is now just one space after punctuation, not two. Typewriter spacing used to be double spaced due to the difficulty in reading the type.
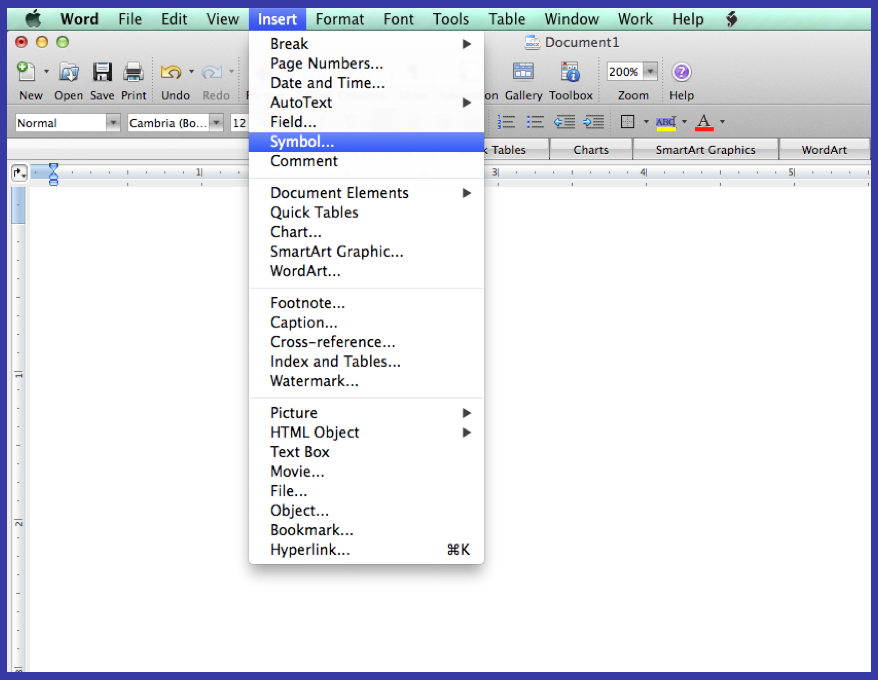
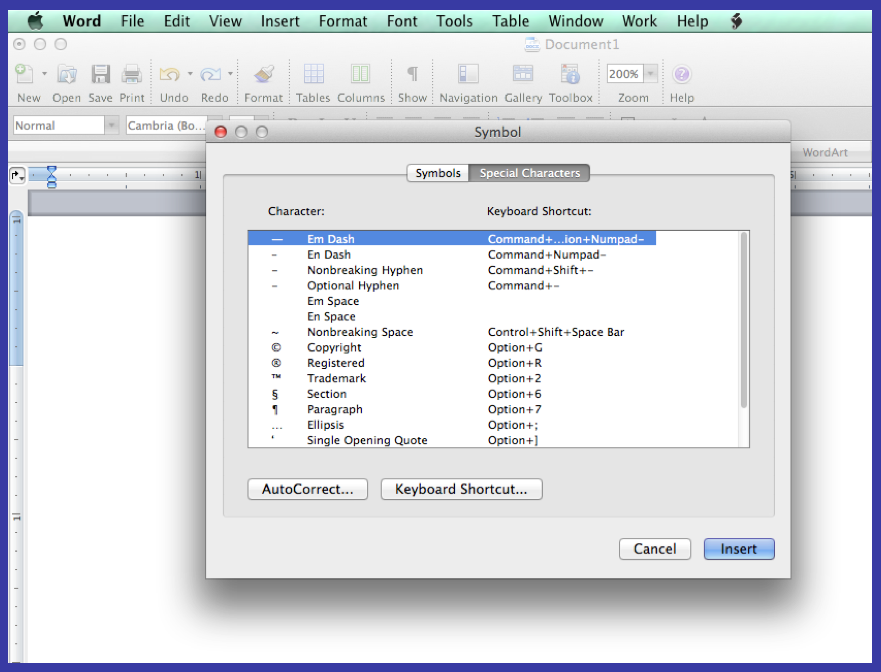
- Dashes—Use “em-dashes” (ie: —) to replace commas or for pauses in sentences. Do not mix commas with em-dashes in the same sentence. [Wrong: Kelly’s heart was beating so fast, like a snare drum—that she felt it was going to burst. Right: Kelly’s heart was beating so fast—like a snare drum—that she felt it was going to burst.] Keep it consistent. Use “en-dashes” (ie: –) to replace the word “to” such as between dates or a range of numbers (ie: 1882–1904). Only use short hyphen dashes (ie: -) as hyphens. Dashes can be inserted using Microsoft Word by going to “Insert” ? “Symbol” and clicking on the “Special Character” tab. The first two choices are em and en dashes.

- Underlines and ALL CAPS— Underlines and ALL CAPS alone or combined with bold type are taboo. Try to avoid underlining if at all possible. Instead, italicize the word or bold it (or both). If you must have an underline, make sure you have a good reason such as using underlines for key reference words if there are many other formatting types already being used in the same sentence or paragraph. This helps keep your book interior clean and easy to read. ALL CAPS indicates that the author is “screaming,” so make sure you have a good reason to use them, such as a character shouting something.
- General spelling—Be sure to read through your manuscript thoroughly for spelling errors, as the word processing program will not catch them all. The most common errors that your spell checker may not find include misuse of the words “then” and “than,” “there” and “their,” “it’s” and “its,” etc.
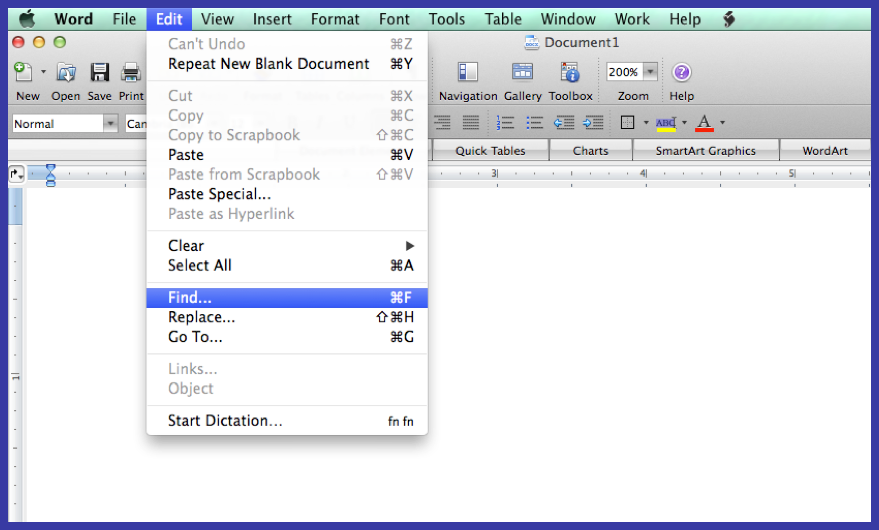
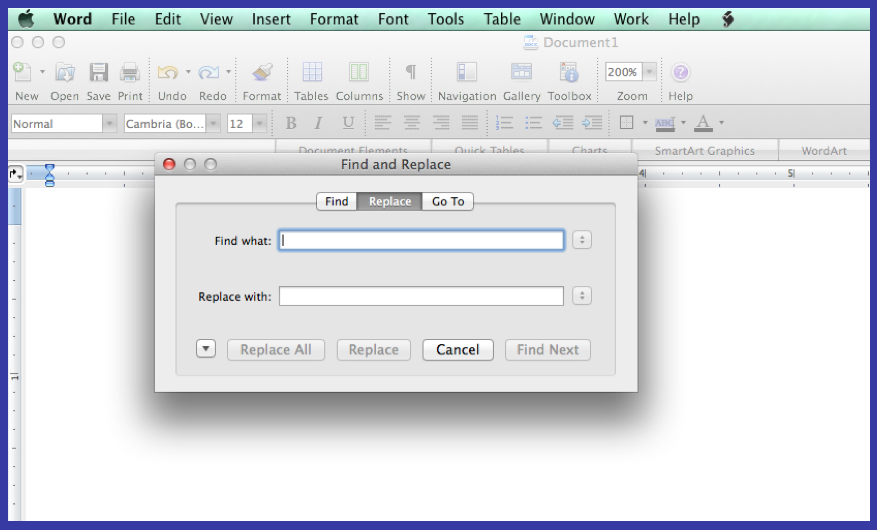
- Find-and-Replace—Word processing programs make it easy to catch most of these errors. Hold down “Ctrl” and “F” at the same time for the “find” action. Click the “Replace” tab. For example, to replace all double spaces (there should be no double spaces in a manuscript) type two spaces in the “Find What” space, then type one space in the “Replace with” space. Click “Replace” and Microsoft Word will automatically find and replace all those errors. This works with words you or your typist may consistently misspell as well.

- Permissions—If you want to use a quote, scripture verses, or other previously published material in your book, you must obtain permission from the owner or copyright holder of that material. Certain material may be considered public domain, in which case, you do not need permission to use it. However in those instances, it’s still best to cite the source. If you’re not sure, search to see if it can be verified that it is public domain. If the quote you want to use is not public domain, contact the publisher and/or author of the work to be quoted for permission to use it. Publishers have different procedures for obtaining permission to use material that is copyrighted. Most won’t charge for the use, but it’s still important to go through the proper steps so you won’t run into any legal issues later.
In conclusion, when preparing your manuscript for editing, clarity and consistency are key. If the manuscript’s format isn’t consistent, it will look amateur and unprofessional. Unfortunately, unedited (or poorly edited) books have contributed heavily to the “bad name” of self-publishing. The good news is, that trend is changing! Once again, when unsure of anything, check The Chicago Manual of Style, which outlines the current editorial style guidelines for professional-looking books.
